Radiance Cascades For 2D Global Illumination
Radiance Cascades is a novel approach to both 2D and 3D global illumination created by Alexander Sannikov (the original source article can be found here). It is built to produce a noiseless result by sampling and interpolating incoming radiance from a hierarchy of probes placed on the scene. Each hierarchy level/cascade samples the scene with a higher angular frequency (more rays per probe) and reduced spatial frequency (less probes overall). This project uses my custom OpenGL engine (OPEngine) to implement this technique in 2D in order to explore its intricacies.

Radiance Cascades
The radiance cascades technique is actually only concerned about a data structure for storing and interpolating incoming radiance than how to actually sample this data, but its important to keep in mind that the the radiance probes have to placed uniformly through the scene. The image below represents how the probes are placed on the scene. The first cascade is represented in orange. Each probe casts 4 rays from its origin and in a very short range. The second cascade is represented in green and each probe casts 4 times more rays, but there are 4 times less probes (which doubles the probe separation) and they cast rays twice as far from the orgin (but also start farther away from it). The third cascade is represented in blue and keeps all these scaling factors, casting more rays further away but with less probes.
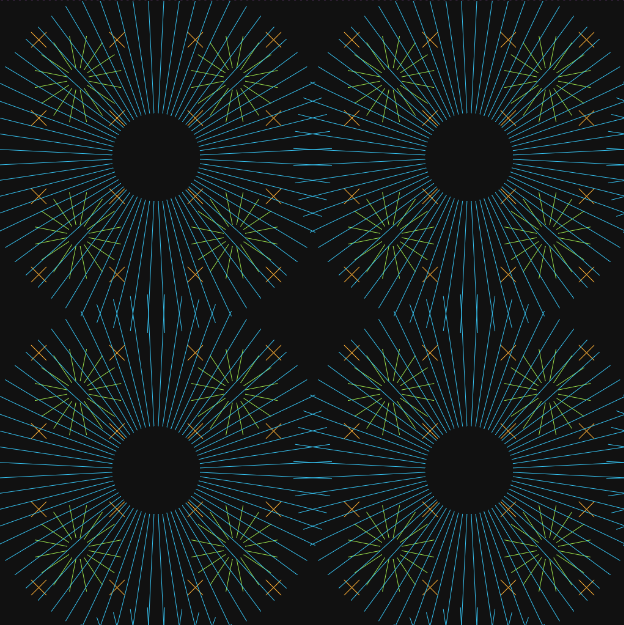 This image along with some useful demos about this technique can be found here.
This image along with some useful demos about this technique can be found here.
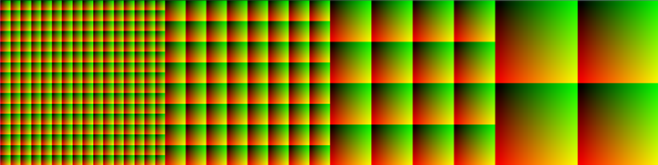
The data sampled by all probes is laid out into 2D textures similar to the layout below, where each texel would finally store the color sampled by a ray from a probe. In this image, we are representing the data from 4 cascades. The first one containing 16 x 16 probes, the second with 8 x 8 and so on. Notice how each cascade uses the same amount of memory of the previous one, since each probe casts 4 times more rays but there are 4 times less probes.
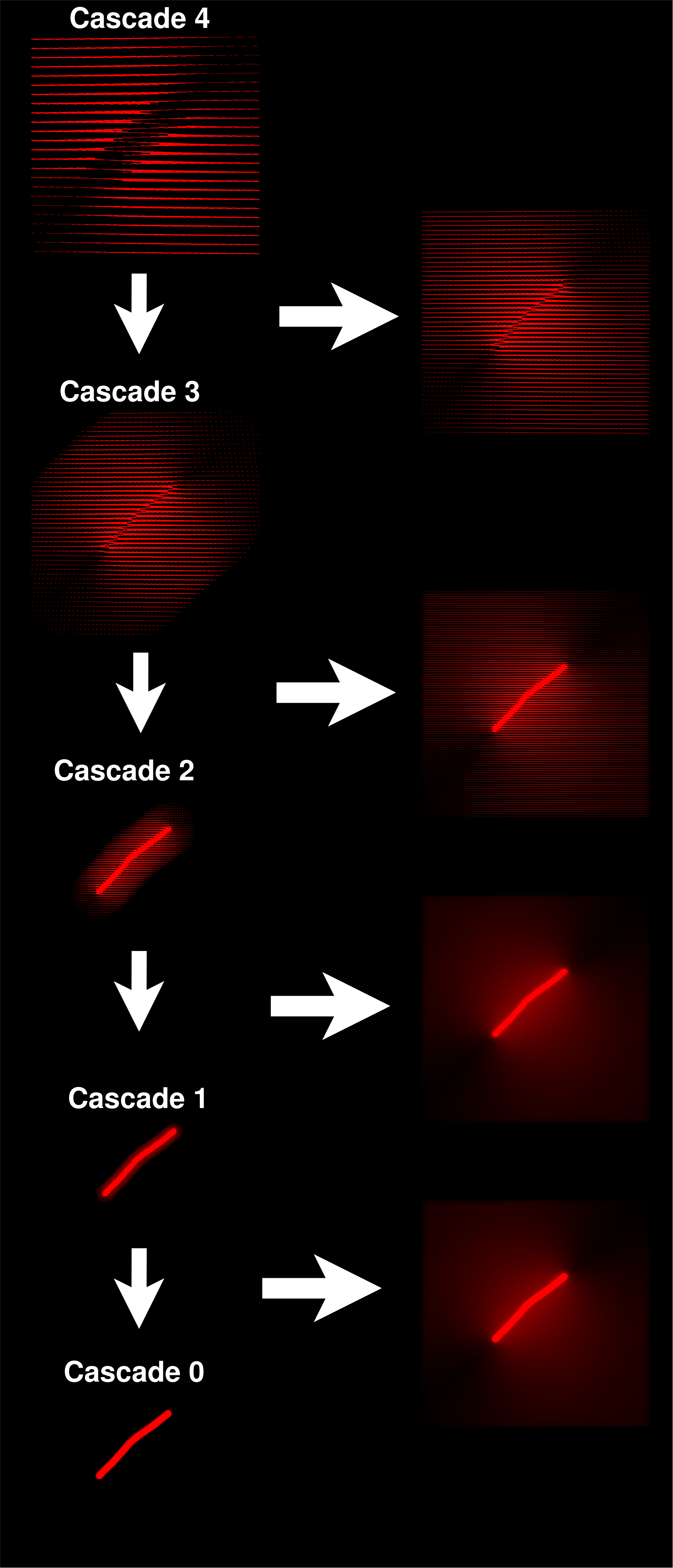
For this project, I have decided to use SDFs drawn with the mouse cursor as the source of radiance. The image below shows the raymarched data the hierarchy of 5 cascades that was used in order to sample the radiance field of the SDF drawing:
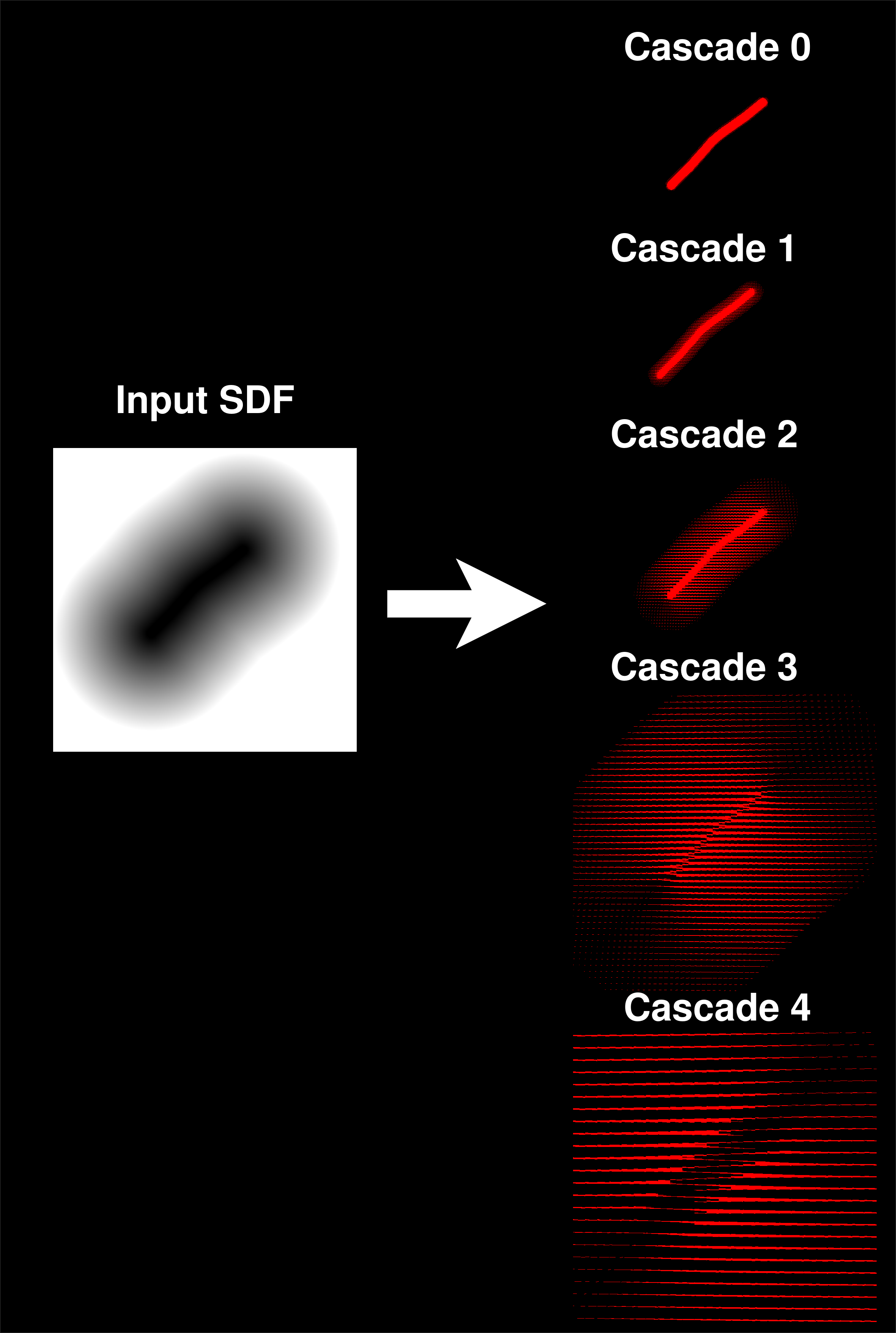
The data from the upper cascades is then added to the lower cascades by using interpolation. For each ray from a probe in the lower cascade, we interpolate the data from the 4 nearest probes, adding up the intepolated radiance from the 4 rays that point into the same direction into the original ray, merging all the data into a single texture.
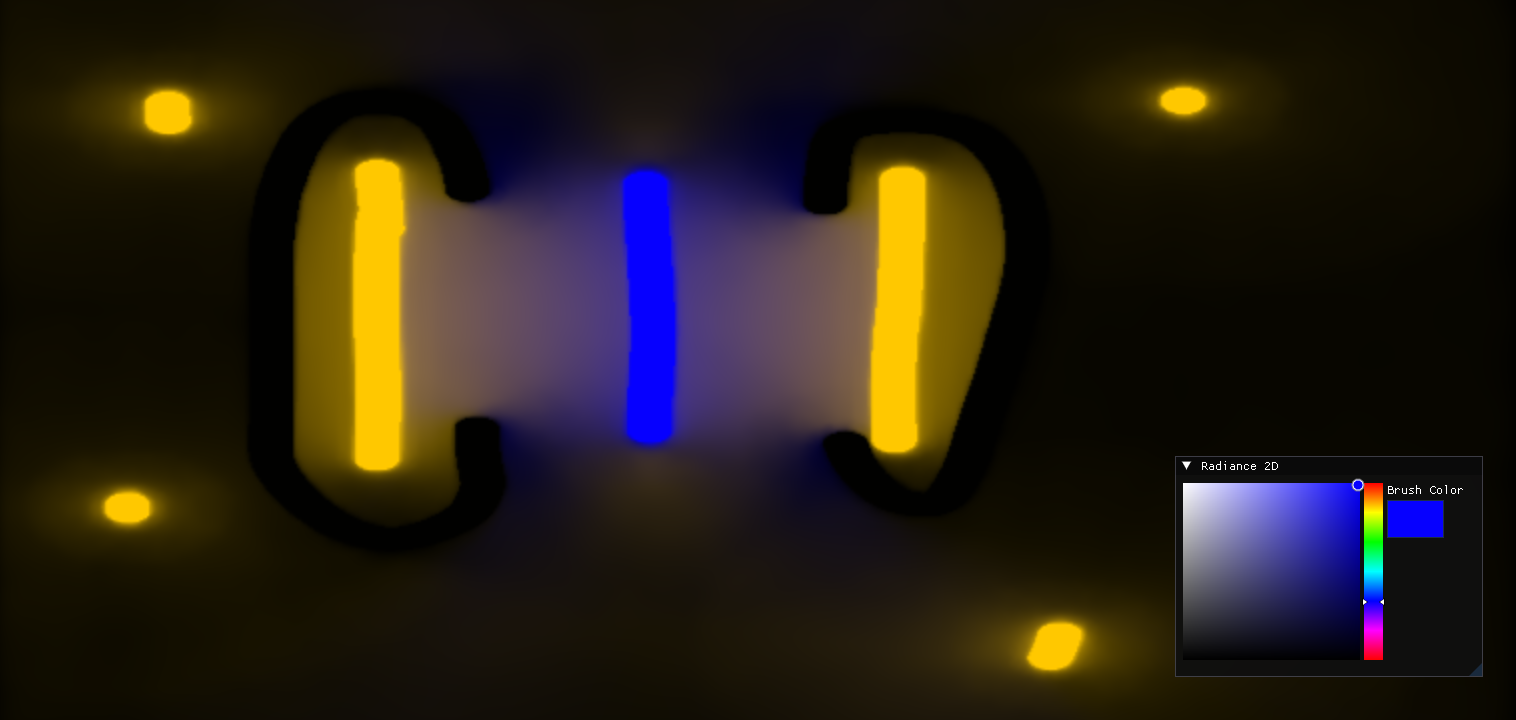
The diffuse lighting can then be calculated by summing the total irradiance on each cascade and the resulting value can be interpolated between probes to form the final render: