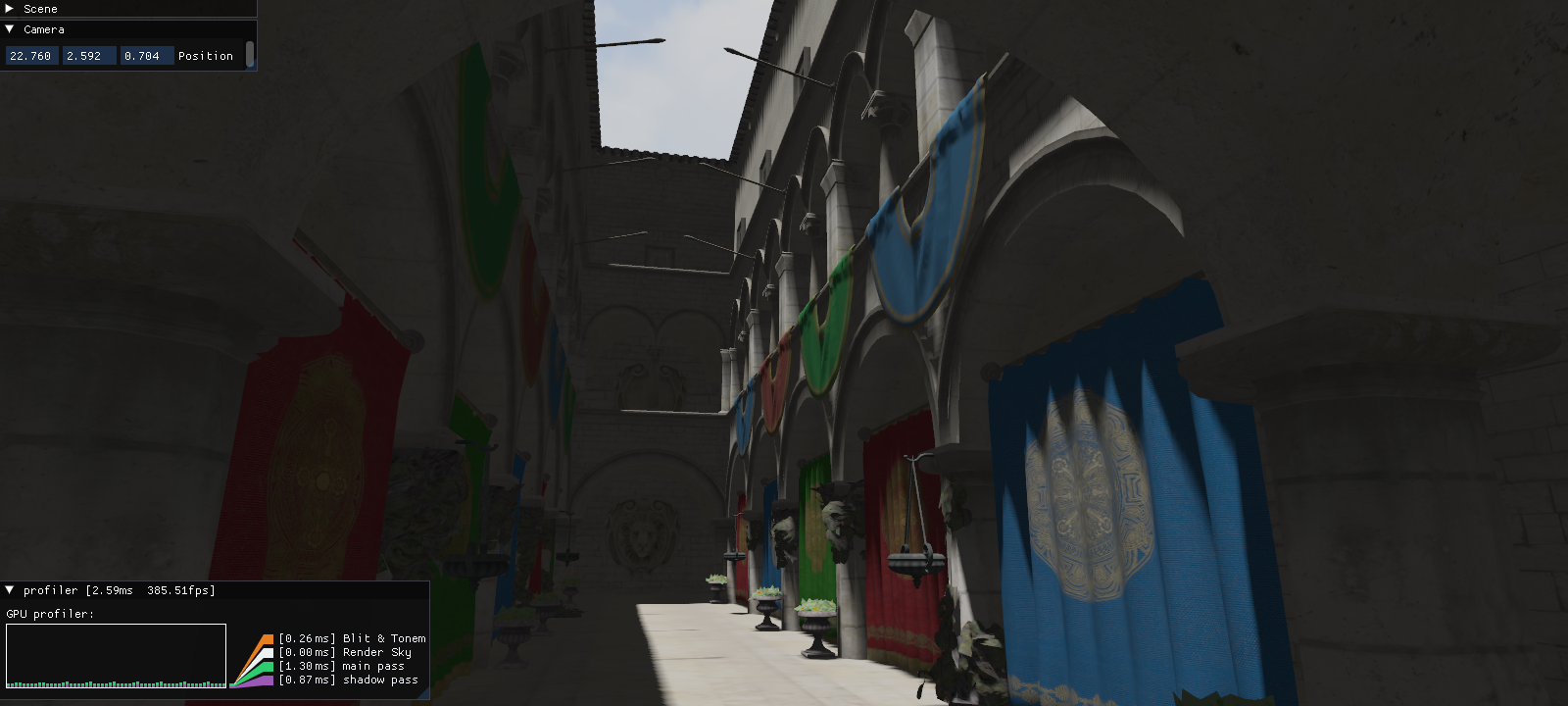
OPEngine
A custom rendering engine based on OpenGL. This engine was used as a base for some of my projects where a lower level API was more convenient. It is meant to be a thin layer of abstraction over OpenGL and comes with a profiler and some tools for handling 3D model/scene loading, shader preprocessing and compilation, uniform buffer bindings, etc...
OPProfiler
Rendering commands can be called inside a task block created by the profiler class:
auto voxelizationTask = profiler->AddTask("voxelization", Colors::belizeHole);
voxelizationTask->Start();
{
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, voxelizationFBO);
// ...
voxelizationShader.UseProgram();
scene->IterateObjects([&](glm::mat4 objectToWorld, std::unique_ptr<MaterialInstance> &materialInstance, std::shared_ptr<Mesh> mesh)
{
// ...
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, mesh->indicesCount, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
})
}
voxelizationTask->End();After registering the task, a timer query is created and the total time for the rendering command will be displayed in the profiler UI:
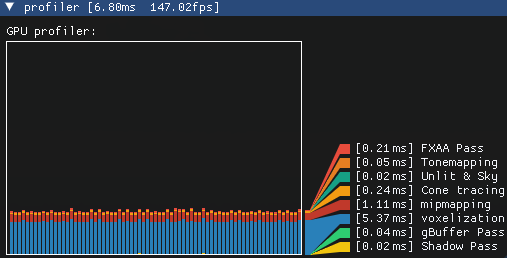
Scene Loading
Scene files are formatted in JSON as seen below:
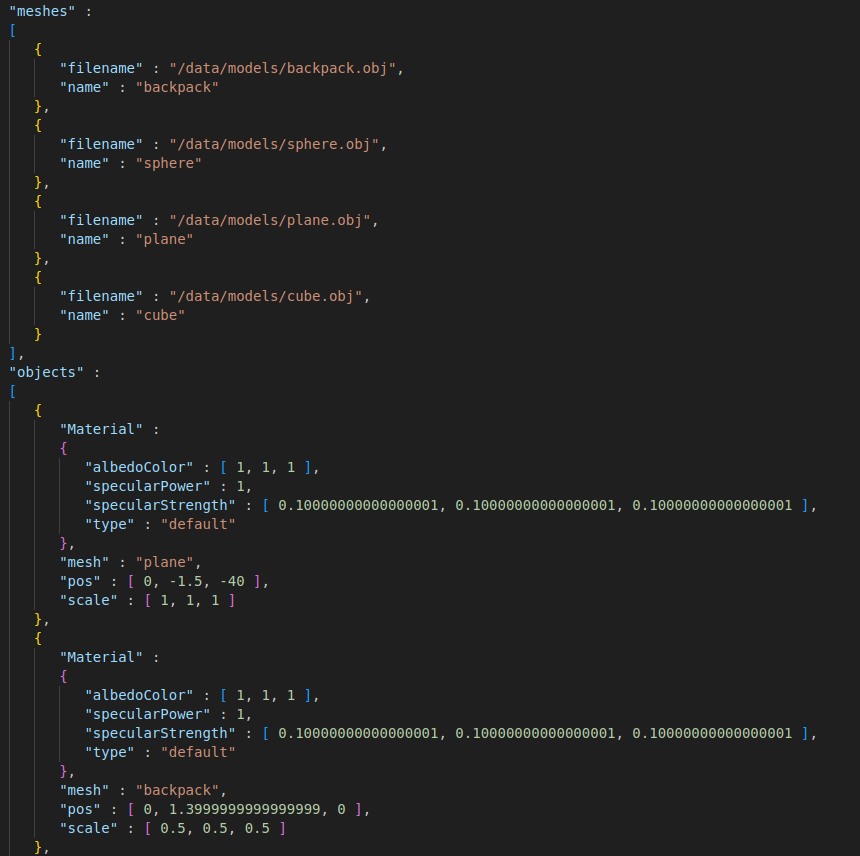
Using the Assimp library, multiple file formats can be used. Multiple models can be imported from the same files. Diffuse, normal and specular maps are supported but the material can be overriten on the scene file by choosing between "default" (the color overridden by the "albedoColor" field), "unlit" and "textured"
Other Features
Registering and setting uniform buffers can be done in a very convenient way by using the ShaderMemoryPool Class:
// Define the buffer on the c++ side
struct GlobalMatrices
{
glm::mat4 projectionMatrix;
glm::mat4 viewMatrix;
glm::mat4 inverseViewMatrix;
};
// Register the buffer into the memory pool
shaderMemoryPool.AddUniformBuffer(sizeof(GlobalMatrices), "GlobalMatrices");
// ...
// After registering all buffers, the bindings can be accessed by any shader after calling BindUniformBlocks()
voxelizationShader = StandardShader(BASE_DIR"/data/shaders/voxelization/voxel.vert", BASE_DIR"/data/shaders/voxelization/voxel.frag");
voxelizationShader.BuildProgram();
voxelizationShader.BindUniformBlocks(bufferBindings);
// ...
auto globalMatricesBuffer = shaderMemoryPool.GetUniformBuffer("GlobalMatrices");
GlobalMatrices *globalMatrices = globalMatricesBuffer->BeginSetData<GlobalMatrices>();
{
globalMatrices->projectionMatrix = projectionMatrix;
globalMatrices->viewMatrix = viewMatrix;
globalMatrices->inverseViewMatrix = inverseViewMatrix;
globalMatrices->voxelMatrix = voxelMatrix;
globalMatrices->inverseVoxelMatrix = invVoxelMatrix;
}
globalMatricesBuffer->EndSetData();The shader class also supports adding extra shader stages (like geometry and tesselation shaders), preprocessor defines set on the c++ side and an aditional preprocessing step takes care of #include directives for glsl shaders.

